|
|
3 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| baseline | 3 years ago | |
| data | 3 years ago | |
| images | 3 years ago | |
| outputs | 3 years ago | |
| presentation | 3 years ago | |
| prompt-learning | 3 years ago | |
| proposal | 3 years ago | |
| utils | 3 years ago | |
| writing/latex | 3 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 3 years ago | |
| ANALYSIS.md | 3 years ago | |
| LICENSE | 3 years ago | |
| README.md | 3 years ago | |
| set_env.sh | 3 years ago | |
| thesis.pdf | 3 years ago | |
| unset_env.sh | 3 years ago | |
README.md
Table of Contents
- Prompt-based methods for Dialog State Tracking
- Dataset
- Environment Setup
- Baseline Experiments
- Install the requirements
- Train the baseline model
- Belief State Prediction
- Baseline Evaluation
- Results from baseline experiments
- Prompt Learning Experiments
- Install the requirements
- Training Data
- Value Extraction
- Train the prompt model
- Belief State Generations (Prompt-based slot generation)
- Evaluation of prompt-based generations
- Results from prompt-based belief state generations
- Multi-prompt Learning Experiments
- Analysis
Prompt-based methods for Dialog State Tracking
Repository for my master thesis at the University of Stuttgart (IMS).
Proposal PDF - with detailed explanation of thesis experiments
Presentation PDF - slides from the thesis presentation
Thesis PDF - details about methods, experiments, results, discussion
Dataset
MultiWOZ 2.1 dataset is used for training and evaluation of the baseline/prompt-based methods. Only single-domain dialogues are used in this setup for training and testing. Each dialogue contains multiple turns and may also contain a subdomain booking. Five domains - Hotel, Train, Restaurant, Attraction, Taxi are used in the experiments and excluded the other two domains as they only appear in the training set. Under few-shot settings, only a portion of the training data is utilized to measure the performance of the DST task in a low-resource scenario.
| Data Split | # Dialogues | # Total Turns |
|---|---|---|
| 5-dpd | 25 | 100 |
| 10-dpd | 50 | 234 |
| 50-dpd | 250 | 1114 |
| 100-dpd | 500 | 2292 |
| 125-dpd | 625 | 2831 |
| 250-dpd | 1125 | 5187 |
| valid | 190 | 900 |
| test | 193 | 894 |
In the above table, term "dpd" refers to "dialogues per domain". For example, 50-dpd means 50 dialogues per each domain.
All the training and testing data can be found under /data/ folder.
Environment Setup
Python 3.6 is required for training the baseline model. Python 3.10 is required for training the prompt-based model. conda is used for creating the environments.
Use CONDA_ENVS_PATH to set the custom path for storing the conda environments (if required)
# optional
export CONDA_ENVS_PATH=/path/to/custom/dir
Create conda environment (for baseline model)
Create an environment for baseline training with a specific python version (Python 3.6 is required).
conda create -n <baseline-env-name> python=3.6
Create conda environment (for prompt learning)
Create an environment for prompt-based methods (Python 3.10 is required)
conda create -n <prompt-env-name> python=3.10
Activate the conda environment
To activate the conda environment, run:
conda activate <env-name>
Deactivating the conda environment
To deactivate the conda environment, run: (Only after running all the experiments)
conda deactivate
Download and extract SOLOIST pre-trained model
Download and unzip the pretrained model, this is used for fine-tuning the baseline and prompt-based methods. For more details about the pre-trained SOLOIST model, refer to the GitHub repo.
Download the zip file, replace the /path/to/folder from the below command to a folder of your choice.
wget https://bapengstorage.blob.core.windows.net/soloist/gtg_pretrained.tar.gz \ -P /path/to/folder/
Extract the downloaded pretrained model zip file.
tar -xvf /path/to/folder/gtg_pretrained.tar.gz
Clone the repository
Clone the repository source code
git clone https://git.pavanmandava.com/pavan/master-thesis.git
Change directory
cd master-thesis
Pull the changes from remote (if local is behind the remote)
git pull
Set Environment variables
Next step is to set environment variables that contains path to pre-trained model, saved models and output dirs.
Edit the set_env.sh file and set the paths (as required) for the following:
PRE_TRAINED_SOLOIST - Path to the extracted pre-trained SOLOIST model
SAVED_MODELS_BASELINE - Path for saving the trained baseline models (fine-tuning) at checkpoints
OUTPUTS_DIR_BASELINE - Path for storing the baseline model outputs (belief state predictions)
SAVED_MODELS_PROMPT - Path for saving the trained prompt-based models (after each epoch)
OUTPUTS_DIR_PROMPT - Path for storing the prompt model outputs (generations)
ℹ️ Note: Change the path for each environment variable and make sure it matches with your local system. Invalid/Wrong paths may lead to errors while running the training/testing script.
nano set_env.sh
Save the edited file and source it
source set_env.sh
Run the below line to unset the environment variables (when done with experiments)
sh unset_env.sh
Baseline Experiments
SOLOIST (Peng et al., 2021), the baseline model for this thesis, is a task-oriented dialog system that uses transfer learning and machine teaching to build task bots at scale. SOLOIST uses the pre-train, fine-tune paradigm for building end-to-end dialog systems using a transformer-based auto-regressive language model GPT-2. In the pre-training stage, SOLOIST is initialized with 12-layer GPT-2 (117M parameters) and further trained on two task-oriented dialog corpora for solving belief state prediction task. In the fine-tuning stage, the pre-trained SOLOIST is fine-tuned on MultiWOZ 2.1 dataset to perform belief prediction task.
Install the requirements
After following the environment setup steps in the previous section, install the required python modules for baseline model training.
Change directory to baseline and install the requirements. Make sure the correct baseline conda environment is activated before installing the requirements.
cd baseline
pip install -r requirements.txt
Train the baseline model
Train a separate model for each data split. Edit the train_baseline.sh file to modify the hyperparameters while training (learning rate, epochs). Use CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES to specify a CUDA device (GPU) for training the model.
sh train_baseline.sh -d <data-split-name>
Pass the data split name to -d flag. Possible values are: 5-dpd, 10-dpd, 50-dpd, 100-dpd, 125-dpd, 250-dpd
Example training command: sh train_baseline.sh -d 50-dpd
Belief State Prediction
Choose a checkpoint of the saved baseline model to generate belief states.
Set the MODEL_CHECKPOINT environment variable with the path to the chosen model checkpoint. It should only contain the path from the "experiment-{datetime}" folder.
export MODEL_CHECKPOINT=<experiment-folder>/<data-split-name>/<checkpoint-folder>
Example: export MODEL_CHECKPOINT=experiment-20220831/100-dpd/checkpoint-90000
Generate belief states by running decode script
sh decode_baseline.sh
The generated predictions are saved under OUTPUTS_DIR_BASELINE folder. Some of the generated belief state predictions are uploaded to this repository and can be found under outputs folder.
Baseline Evaluation
The standard Joint Goal Accuracy (JGA) is used to evaluate the belief predictions. This metric compares all the predicted belief states to the ground-truth states for each turn. The prediction is considered correct only if all the predicted belief states match with the ground-truth states. Both slots and values must match for the prediction to be correct.
Edit the evaluate.py to set the predictions output file before running the evaluation
python evaluate.py
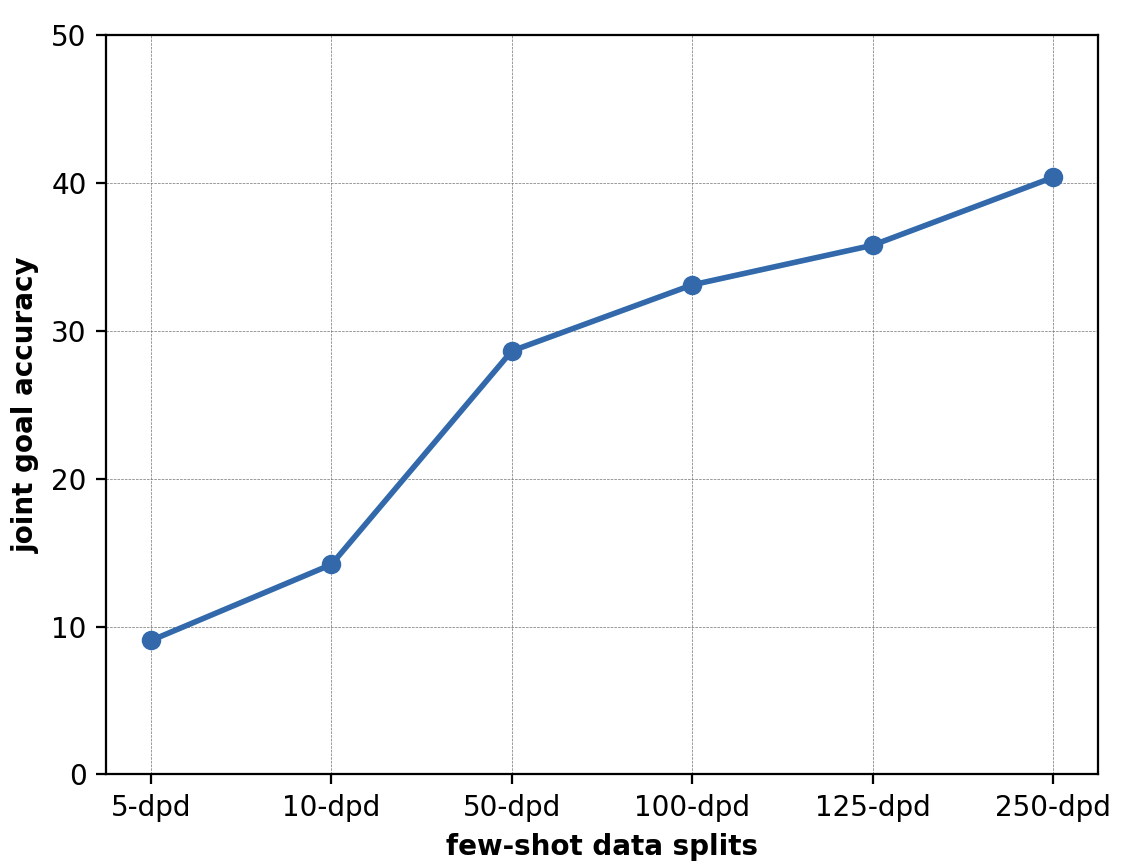
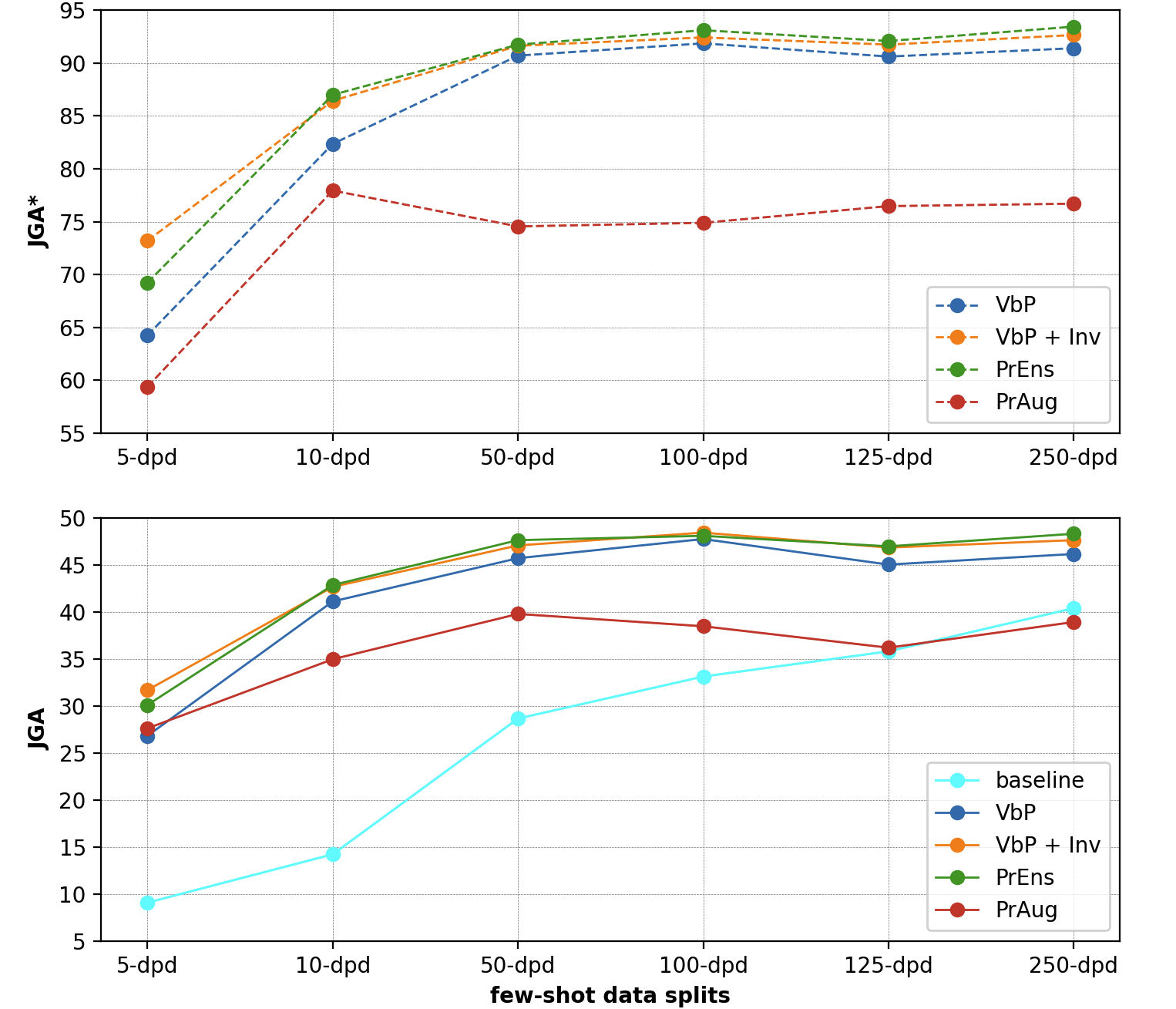
Results from baseline experiments
| data-split | JGA |
|---|---|
| 5-dpd | 9.06 |
| 10-dpd | 14.20 |
| 50-dpd | 28.64 |
| 100-dpd | 33.11 |
| 125-dpd | 35.79 |
| 250-dpd | 40.38 |
Prompt Learning Experiments
Install the requirements
After following the environment setup steps in the previous section, install the required python modules for prompt model training.
Change directory to prompt-learning and install the requirements. Make sure the correct prompt-learning conda environment is activated before installing the requirements.
cd prompt-learning
pip install -r requirements.txt
Training Data
The data for training the prompt learning model is available under data/prompt-learning directory.
create_dataset.py (link) has the scripts for converting/creating the data for training the prompt-based model.
Value Extraction
Value candidates are extracted from the user dialog history and are utilized in the testing/inference phase. These extracted values are given to the value-based prompt for generating slots at inference time. Stanford CoreNLP (stanza package) is used to first extract POS tags and named entities. A set of rules are used to extract values from POS tags and named entities:
- Adjectives (
JJ) and Adverbs (RB) are considered as possible values- Example: expensive, moderate
- Consider previous negator
not- Example: not important (= dont care)
- Named entities (place names, time, date/day, numbers)
- Example: 08:30, friday
- Custom set of Regex NER rules for recognizing named entities
- Stop words and repeated candidate values are filtered out
Note: Running
create_dataset.pycan take some time as it needs to download, install and run Stanford CoreNLPstanzapackage. This script also downloads coreNLP files of size about~1GBand requires significant amount of RAM and processor capabilities to run it efficiently.All the data required for training the prompt-based model is already available under the data directory of this repo. For reproducing the results, it's not required to run this script.
Train the prompt model
Train a separate model for each data split. Edit the train_prompting.sh file to modify the default hyperparameters for training (learning rate, epochs).
sh train_prompting.sh -d <data-split-name>
Pass the data split name to -d flag.
Possible values are: 5-dpd, 10-dpd, 50-dpd, 100-dpd, 125-dpd, 250-dpd
Example training command: sh train_baseline.sh -d 50-dpd
Some train_prompting.sh flags:
--num_epochs - Number of epochs
--learning_rate - Initial learning rate for Optimizer
--with_inverse_prompt - Use Inverse Prompt while training (recommended)
--inverse_prompt_weight - Weight of the inverse prompt for loss function
Note: The defaults in train_prompting.sh are the best performing values.
Belief State Generations (Prompt-based slot generation)
Now, the belief states can be generated by prompting. Choose a prompt fine-tuned model from the saved epochs and run the below script to generate belief states.
Generate belief states by running the below script:
sh test_prompting.sh -m <tuned-prompt-model-path>
The argument -m takes the relative path of saved model from SAVED_MODELS_PROMPT env variable. It takes the following structure -m <data-split-name>/<experiment-folder>/<epoch-folder>
Example: sh test_prompting.sh -m 50-dpd/experiment-20221003T172424/epoch-09
The generated belief states (outputs) are saved under OUTPUTS_DIR_PROMPT folder. Some of the output files are uploaded to this repository and can be found under outputs folder.
Evaluation of prompt-based generations
The standard Joint Goal Accuracy (JGA) is used to evaluate the belief state predictions. In order to exclude the influence of wrongly extracted values, JGA* is computed only for values that are extracted correctly at each turn.
The evaluate.py file can be used to verify the below JGA scores.
cd prompt-learning
python evaluate.py -o path/to/outputs/file
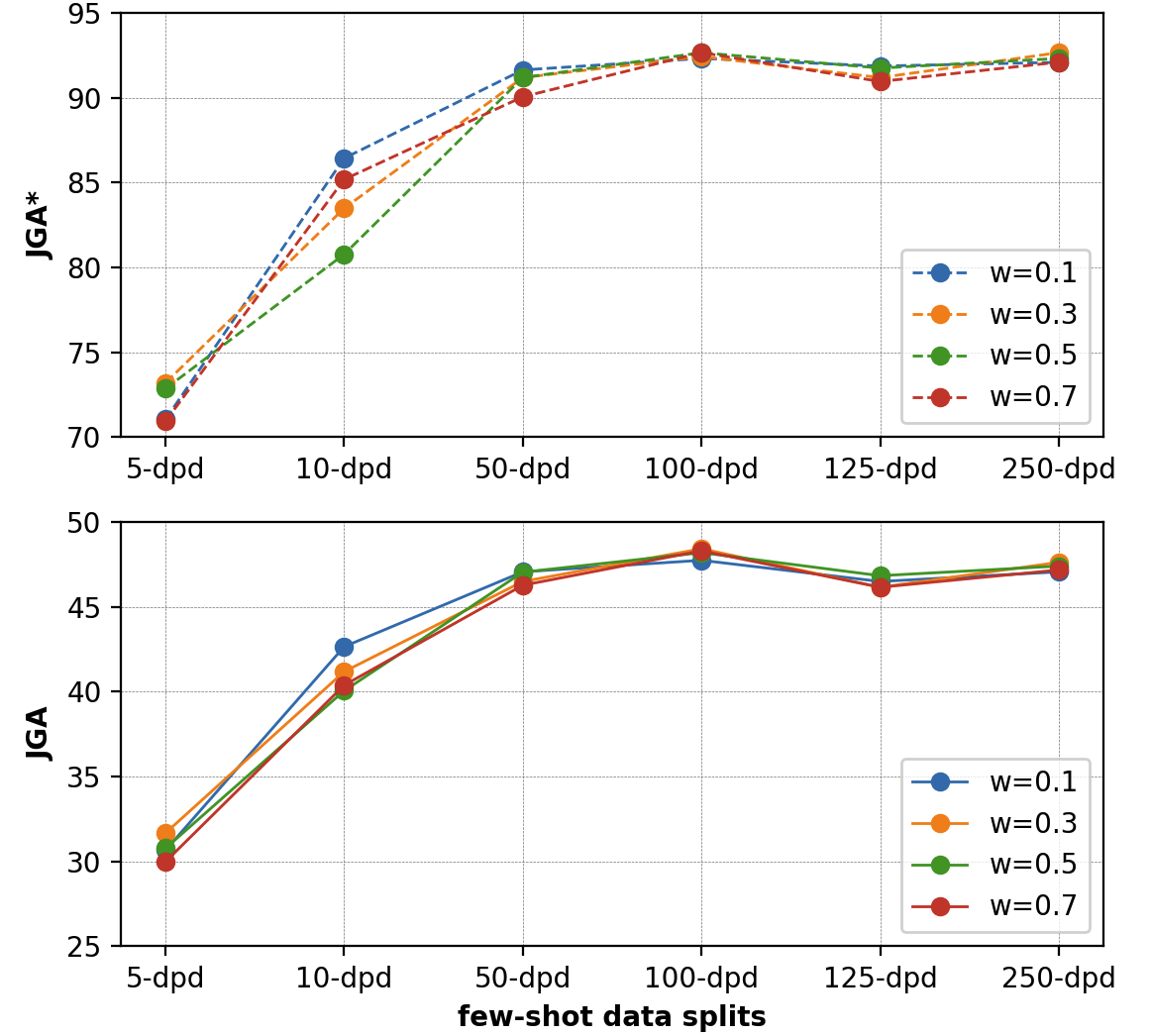
Results from prompt-based belief state generations
| w = 0.1 | w = 0.3 | w = 0.5 | w = 0.7 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | JGA | JGA* | JGA | JGA* | JGA | JGA* | JGA | JGA* |
| 5-dpd | 30.66 | 71.04 | 31.67 | 73.19 | 30.77 | 72.85 | 29.98 | 70.93 |
| 10-dpd | 42.65 | 86.43 | 41.18 | 83.48 | 40.05 | 80.77 | 40.38 | 85.18 |
| 50-dpd | 47.06 | 91.63 | 46.49 | 91.18 | 47.04 | 91.18 | 46.27 | 90.05 |
| 100-dpd | 47.74 | 92.31 | 48.42 | 92.42 | 48.19 | 92.65 | 48.3 | 92.65 |
| 125-dpd | 46.49 | 91.86 | 46.15 | 91.18 | 46.83 | 91.74 | 46.15 | 90.95 |
| 250-dpd | 47.06 | 92.08 | 47.62 | 92.65 | 47.4 | 92.31 | 47.17 | 92.09 |
Multi-prompt Learning Experiments
Prompt Ensemble
In the previous section, only a single value-based prompt is used at training and inference time. In this task, multiple value-based prompts are utilized at training and inference time to leverage the advantages of generation ability from different prompts. This task aims to train a single model with multiple prompts as it is much faster and more memory efficient than having to train a separate model for each prompt (and multiple models at inference time).
| f | prompt functions |
|---|---|
| f1 | belief states: [v] = [s] |
| f2 | [v] is the value of [s] |
| f3 | [v] is of slot type [s] |
| f4 | belief states: value = [s], slot = [s] |
Training
A separate prompt ensemble model is trained for each data split to evaluate the performance of multi-prompt methods in low-resource scenarios. Edit the train_prompting.sh file to add --with_prompt_ensemble flag for training with multiple prompt functions.
The probability of the generated slot (for loss) on multiple prompt functions is calculated by weighted averaging the probability from each prompt function.
Run the training script as before after adding the --with_prompt_ensemble flag:
sh train_prompting.sh -d <data-split-name>
Testing/Slot-generations
While testing (slot-generation), a simple majority voting is used to pick the generated slot from different prompts. When there's no simple majority in the generated slots by multiple prompts, the slot with the highest probability is picked.
Script for generating belief states (slots) using prompt-ensemble remains the same: (there's no need to add any extra flags here, the scripts checks if the model was trained on multiple prompts and uses ensemble prompts for generating)
sh test_prompting.sh -m <saved-model-path>
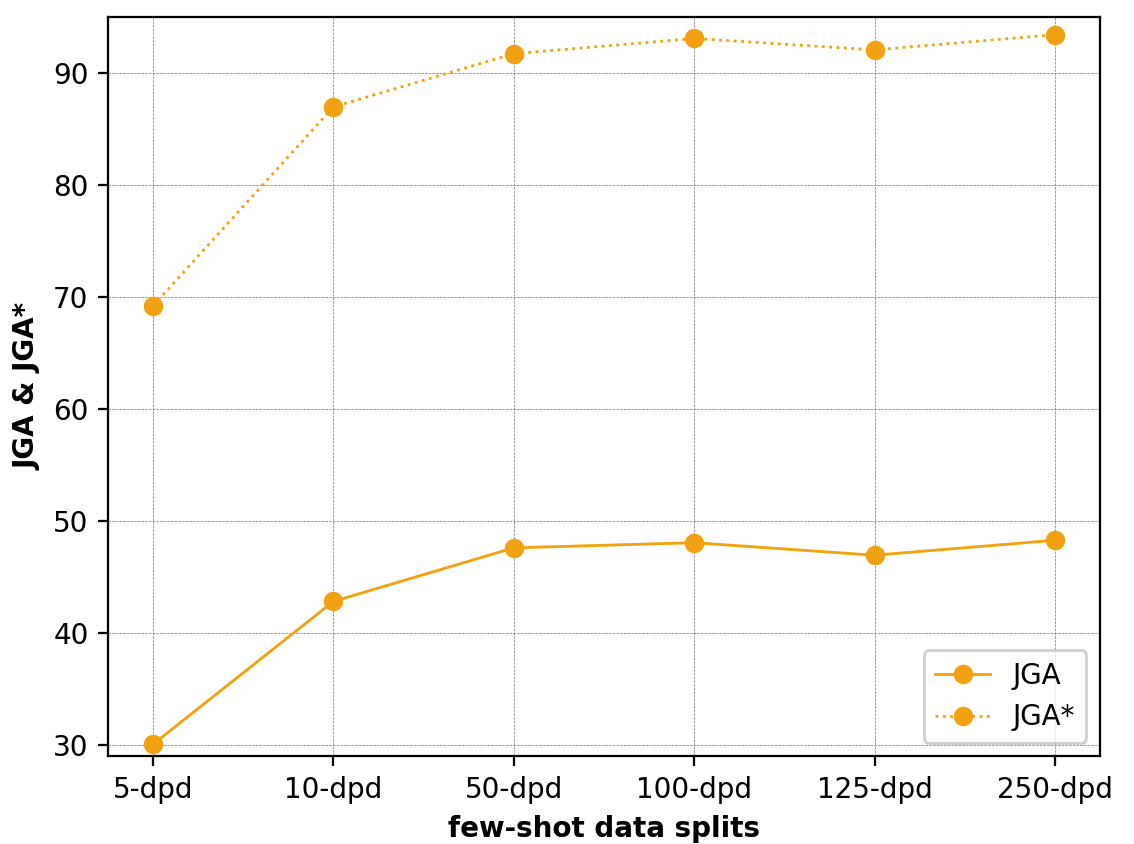
Results from Prompt Ensembling
| Dataset | JGA | JGA* |
|---|---|---|
| 5-dpd | 30.09 | 69.23 |
| 10-dpd | 42.84 | 86.99 |
| 50-dpd | 47.62 | 91.74 |
| 100-dpd | 48.08 | 93.10 |
| 125-dpd | 46.96 | 92.08 |
| 250-dpd | 48.30 | 93.44 |
Prompt Augmentation
Prompt Augmentation, also called demonstration learning, provides a few additional answered prompts that can demonstrate to the PLM, how the actual prompt slot can be answered. Sample selection of answered prompts are hand-crafted and hand-picked manually. Experiments are performed on different sets of answered prompts.
Edit the test_prompting.sh file and add --with_answered_prompts flag for generating slots with answered prompts.
sh test_prompting.sh -m <tuned-prompt-model-path>
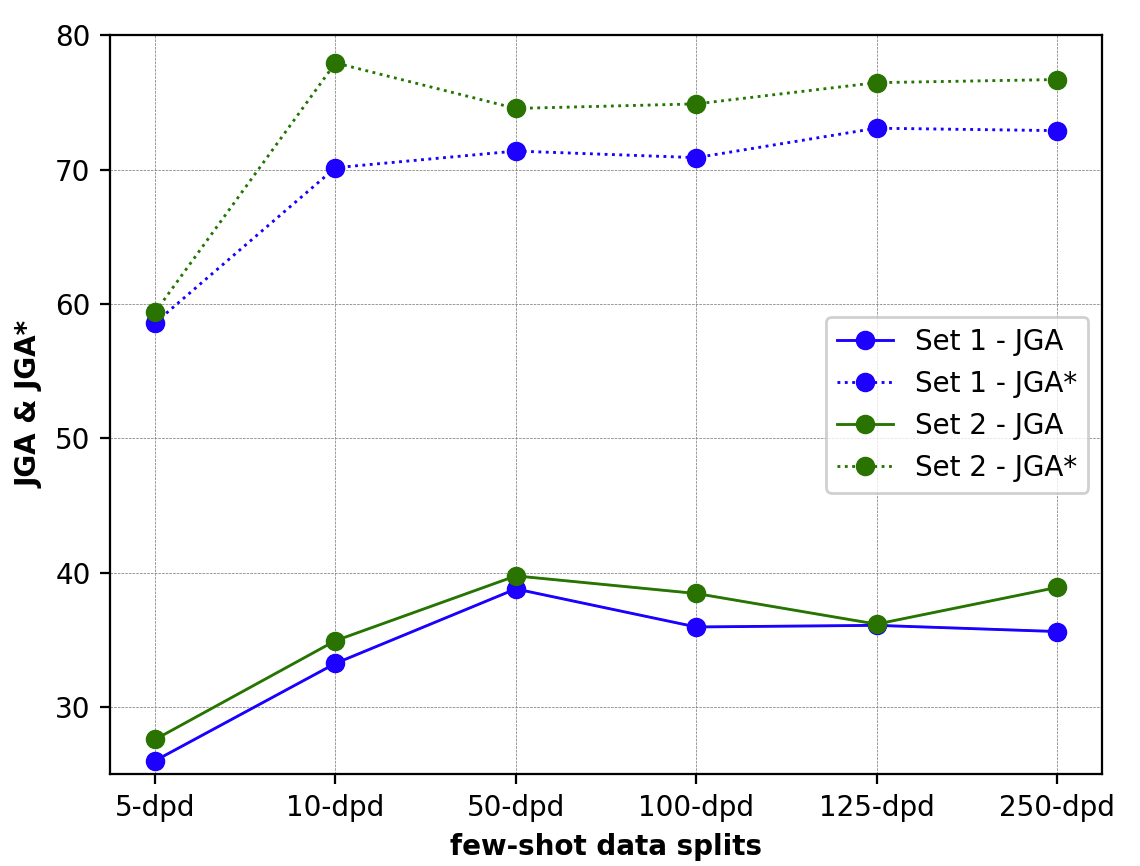
Results from Prompt Augmentation
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | JGA | JGA* | JGA | JGA* |
| 5-dpd | 26.02 | 58.6 | 27.6 | 59.39 |
| 10-dpd | 33.26 | 70.14 | 34.95 | 77.94 |
| 50-dpd | 38.8 | 71.38 | 39.77 | 74.55 |
| 100-dpd | 35.97 | 70.89 | 38.46 | 74.89 |
| 125-dpd | 36.09 | 73.08 | 36.18 | 76.47 |
| 250-dpd | 35.63 | 72.9 | 38.91 | 76.7 |
Comparison of all the results
Analysis
Analyses of the results and belief state generations (outputs) can be found here.